Today, we are constantly blasted with often contradicting information about nutrition. Some people swear by the importance of protein and animal products, while others tell us it's all about the caloric balance. But how can we avoid nutrition deficiencies with our micronutrients in the diet?
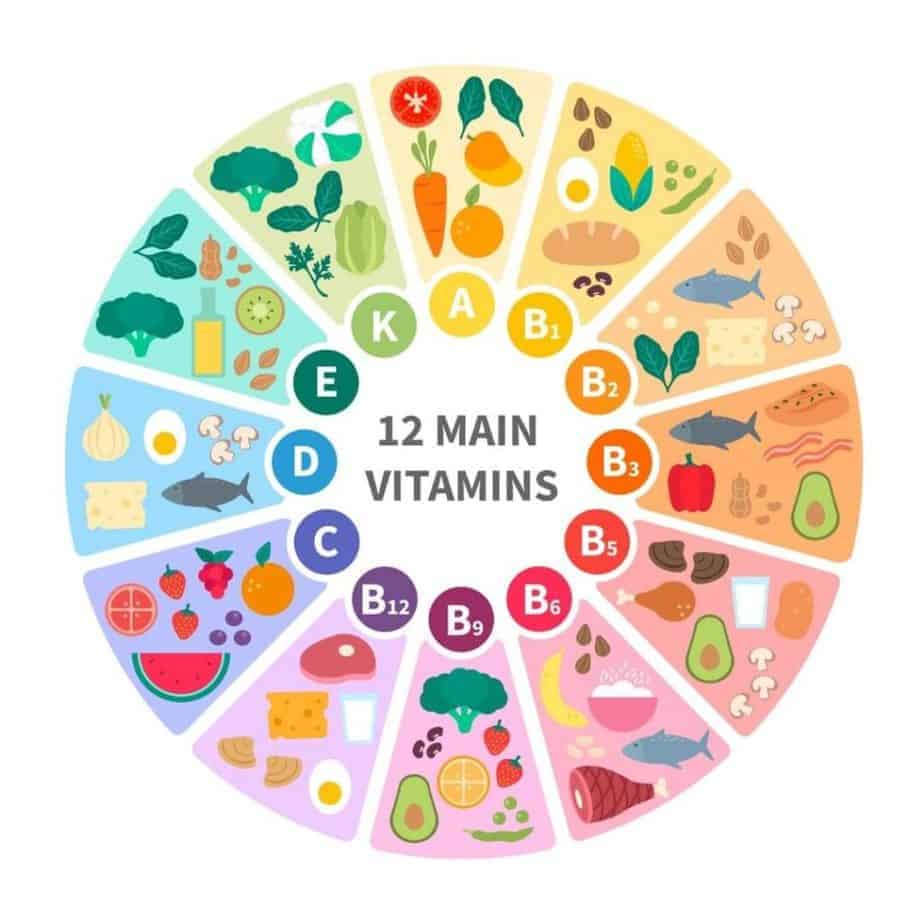

Table of Contents
How Important Are Micronutrients To Prevent Deficiencies In Your Diet?
Now, because fat, protein and carbohydrates are taking the majority of the attention, one thing remains ignored!
That is namely, the importance of micronutrients. Above all the topic of discussion for today!
So without further ado, let us go in depth on micronutrients and discuss what they are, what they do in the body, and what the best sources are!
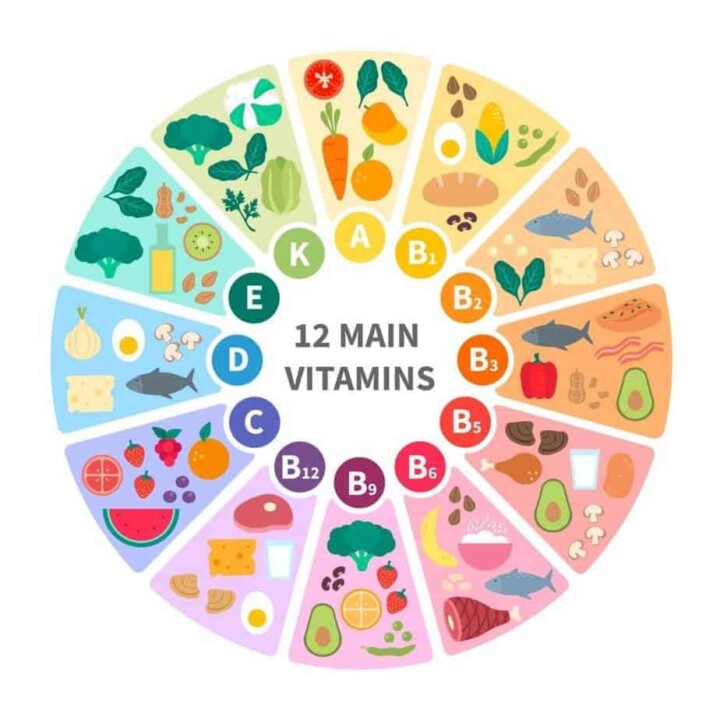
📕 What Is A Micronutrient? Micronutrients Definition!
What are micronutrients exactly? A micronutrient is a vitamin, mineral or other nutrient that the body needs in small amounts to function properly.
Micronutrients are important because they help your cells do their job. With the exception of vitamin D, the body cannot produce micronutrients, so they must come from what you eat.
In today's society, lots of individuals rely on fast food or prepackaged foods with little nutritional content.
So it's no surprise that individuals are more frequently falling short of their micronutrient intake.
⁉️ What Are Essential Micronutrients?
Micronutrients are nutrients that the body needs in small amounts. They include vitamins, minerals, and other substances like amino acids. A deficiency of micronutrients can cause many health problems.
People who do not get enough micronutrients in their diet are at risk of deficiency.
💚 What Causes Micronutrient Deficiencies?
Inadequate intake is the main cause of micronutrient deficiencies. Micronutrients are also lost or destroyed during food processing, storage and cooking.
The body also excretes micronutrients through sweat and urine. Micronutrients are also lost when people eat foods grown in depleted soils.
As you can see, there are many factors that can lead to a micronutrient deficiency.
✅ Factors That Increase Risk Of Micronutrient Deficiencies
The following factors can increase the risk of micronutrient deficiencies.
Poor Eating Habits
Some examples of poor eating habits include eating too much fat, sugar and salt.
Poor Food Preparation Techniques
Certain foods retain better nutrients when eaten raw or steamed, while others are enhanced through certain cooking practices.
For example, the addition of lactic acid while preparing tortillas will make the iron in corn flour more bioavailable.
Beta-carotene (precursor to vitamin A, which is a fat soluble vitamin) is better absorbed with the addition of fats found in olive or coconut oil.
Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Individuals who chronically use alcohol can become deficient in folate, vitamin B6, thiamine, and vitamin A. This is because alcohol disrupts how the body metabolizes nutrients.
Smoking
The influence that smoking has on the way our bodies absorb nutrients is also important. Vitamin C and beta carotene deficiencies are common in individuals who smoke.
Smoking produces free radicals, which cause cell damage, leading to these micronutrient deficiencies.
Medications
Certain medications interfere with the absorption of micronutrients in the body. For example, antibiotics can inhibit vitamin K synthesis, biotin, and zinc.
Additionally, proton pump inhibitors, used to relieve acid reflux, can lead to vitamin B12 malabsorption.
Following Different Restrictive Diets
In addition, practicing a vegan or vegetarian diet and knowing very little about the importance of the proper nutrients to add into their diet to avoid a deficiency.
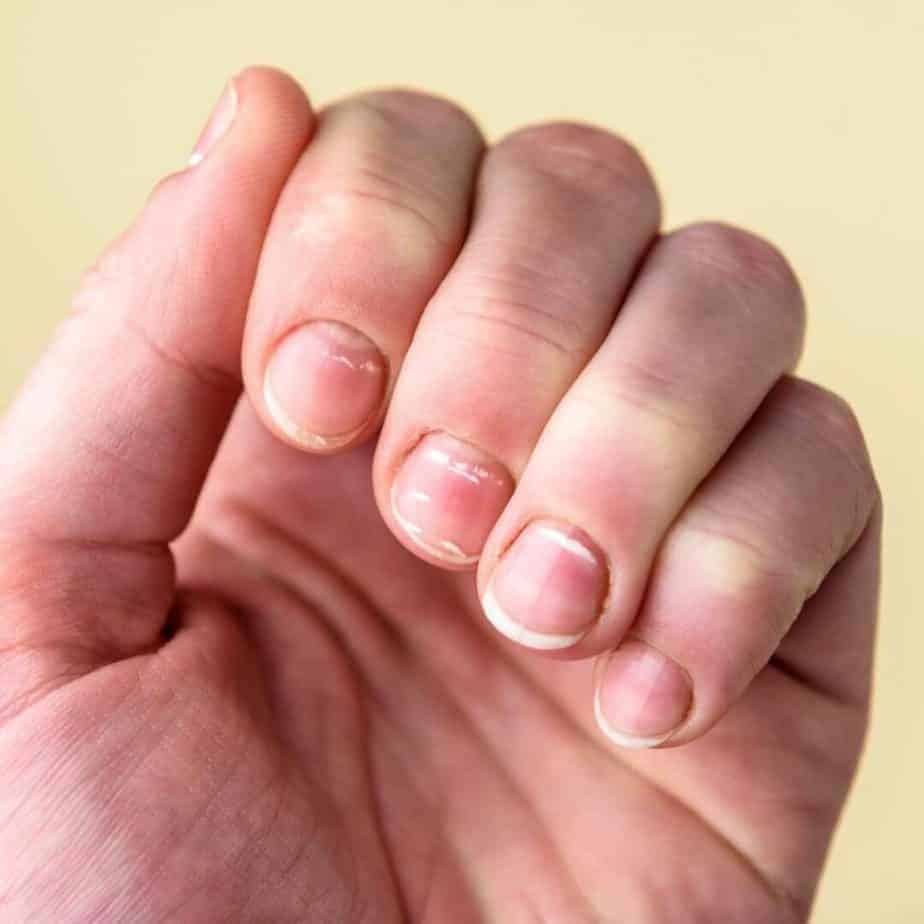
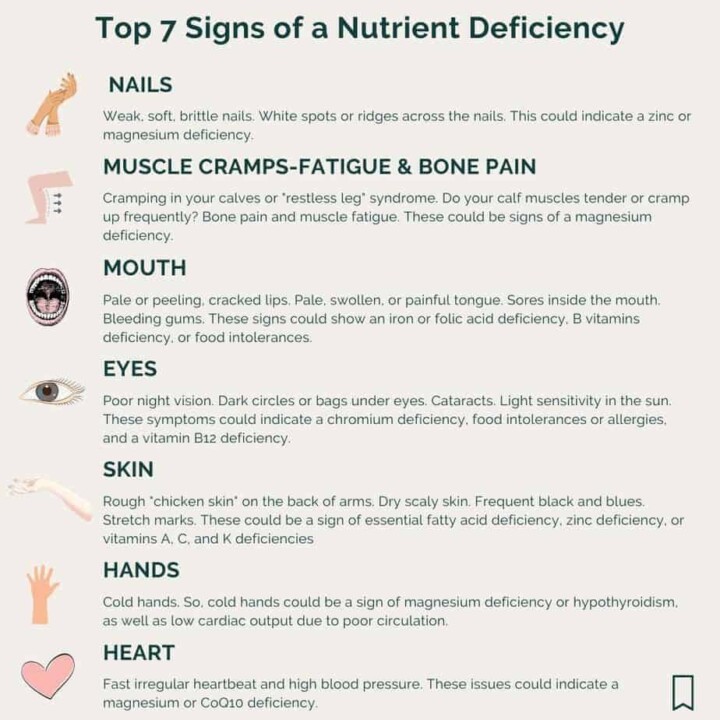
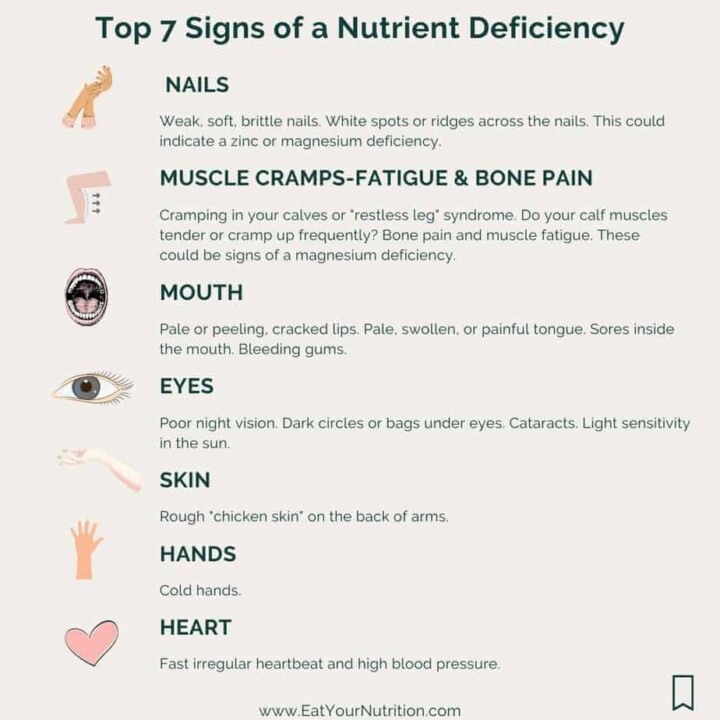
🔝 Top 7 Signs Of A Deficiency in Micronutrients
Here are the top 7 signs to note that you might have a micronutrient deficiency.
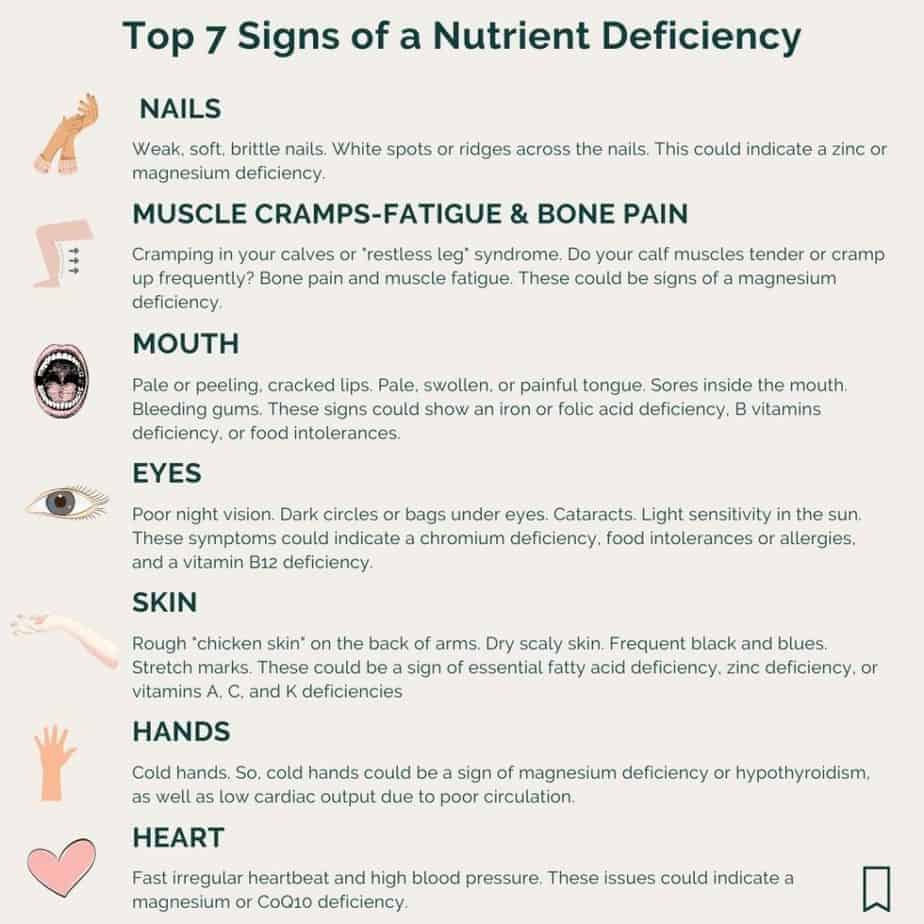
Nails
Weak, soft, brittle nails. White spots or ridges across the nails. This could indicate a zinc or magnesium deficiency.
Muscle Fatigue And Bone Pain
Cramping in your calves or "restless leg" syndrome. Do your calf muscles tender or cramp up frequently? Bone pain and muscle fatigue.
These could be signs of a magnesium deficiency.
Mouth
Pale or peeling, cracked lips. Pale, swollen, or painful tongue. Sores inside the mouth. Bleeding gums.
These signs could show an iron or folic acid deficiency, B vitamins deficiency, or food intolerances.
Eyes
Poor night vision. Dark circles or bags under eyes. Cataracts. Light sensitivity in the sun.
These symptoms could indicate a chromium deficiency, food intolerances or allergies, and a vitamin B12 deficiency.
Skin
Rough "chicken skin" on the back of arms. Dry scaly skin. Frequent black and blues. Stretch marks.
These could be a sign of essential fatty acid deficiency, zinc deficiency, or vitamins A, C, and K deficiencies.
Hands
Cold hands. So, cold hands could be a sign of magnesium deficiency or hypothyroidism, as well as low cardiac output due to poor circulation.
Heart
Fast irregular heartbeat and high blood pressure. These issues could indicate a magnesium or CoQ10 deficiency.
📈 Micronutrients Deficiency Chart
Check out this easy nutrient deficiency chart for a handy reference tool that can help you avoid and become aware of a nutrient deficiency.
Macronutrients Versus Micronutrients
These nutrients provide caloric value and are needed to sustain a healthy body weight and physiological functioning.
On the other hand, micronutrients do not have a caloric value, but are equally important. This is due to their role in various important processes around the body.
So what exactly is the difference between macronutrients and micronutrients when it comes to nutrition?
Well, as the names suggest, macronutrients are the primary nutrients our bodies need in big quantities - protein, fats and carbohydrates.
Micronutrients include phytochemicals, vitamins, minerals, and last but not least, antioxidants! The body needs these nutrients to sustain the production of various enzymes and hormones.
As a result, it relates to the healthy functioning of the organism. Fortunately enough, micronutrient deficiencies are generally easy to diagnose and can be seamlessly treated with various supplements and foods.
🔻 Micronutrient Deficiencies
Though the body needs micronutrients in small amounts, their absence quickly surfaces with a flurry of unwanted side effects.
For example, a magnesium deficiency can cause you to:
- Suffer with poor sleep.
- Cravings for sugar.
- Cramping.
- Be unable to focus during the day. A lack of concentration.
🩺 Common Micronutrient Vitamin And Mineral Deficiencies
With the abundance of nutrient-poor foods that many people survive on, micronutrient deficiencies are common!
Here are the most common micronutrient deficiencies found in humans.
- Vitamin B12
- Iron deficiency
- Iodine
- Magnesium
- Vitamin D
- Folate
Some of these are easy to diagnose and don't hide much risk. However, others can cause severe discomfort and, if sustained in the long term, even damage.
For instance, B12 deficiencies, which are common in vegans and vegetarians, can lead to anemia, memory issues, mood swings, irregular patterns in the heart and even neurological problems.
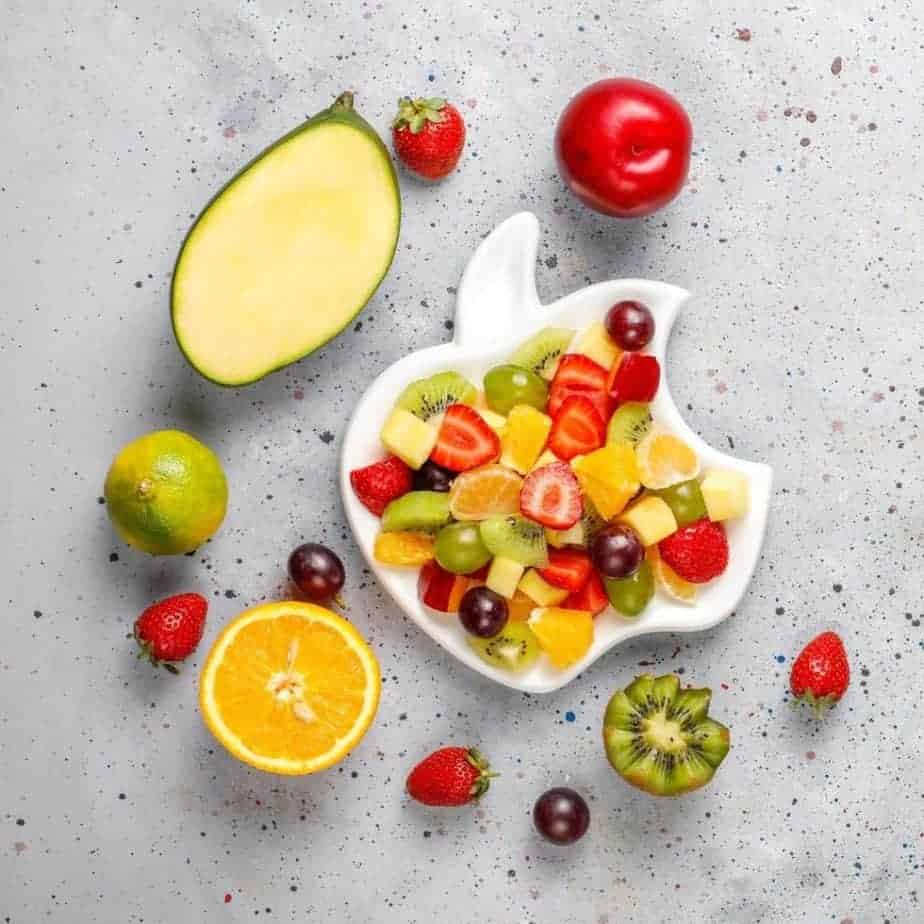

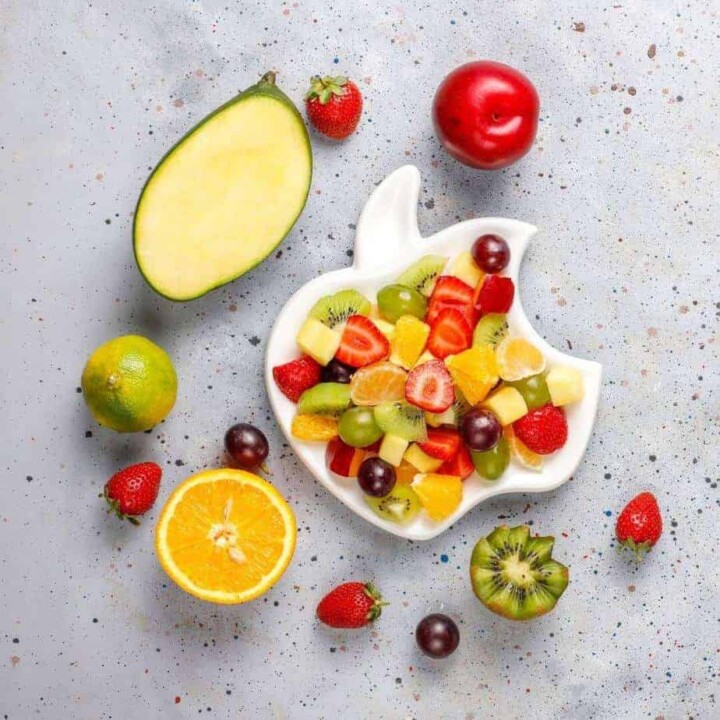
🥗 Micronutrient - Rich Foods
Unless you have severe deficiencies, micronutrient supplements are not mandatory, as most deficiencies can be treated with a slight change in nutritional habits.
💚 Vitamin & Mineral Rich Foods You Should Be Eating!
Let's look at the most vitamin & mineral-abundant foods!
Fatty Fish
The consumption of fatty fish provides the body with omega-3s, and vitamin D.
📥 GET THIS RECIPE IN YOUR INBOX 📥
Citrus Fruits
Foods like oranges and tangerines are rich in vitamin C and folic acid.
Carrots
By adding carrots into your diet, you increase your vitamin A consumption.
Eggs
This tiny protein rich food is full of vitamin B, iron, copper, zinc, manganese, and selenium.
Avocado
Avocado adds tons of healthy fats, but also potassium, magnesium, vitamins B2, B5, B6, and vitamin K.
Kiwi
This delicious fruit is full of vitamin A, C, E, K, folate and choline.
So, including these foods regularly in your menu will keep you away from deficiencies and maintain a balanced inner chemistry.
Don't like diversifying your food sources? Consider speaking to your doctor about micronutrient supplements!
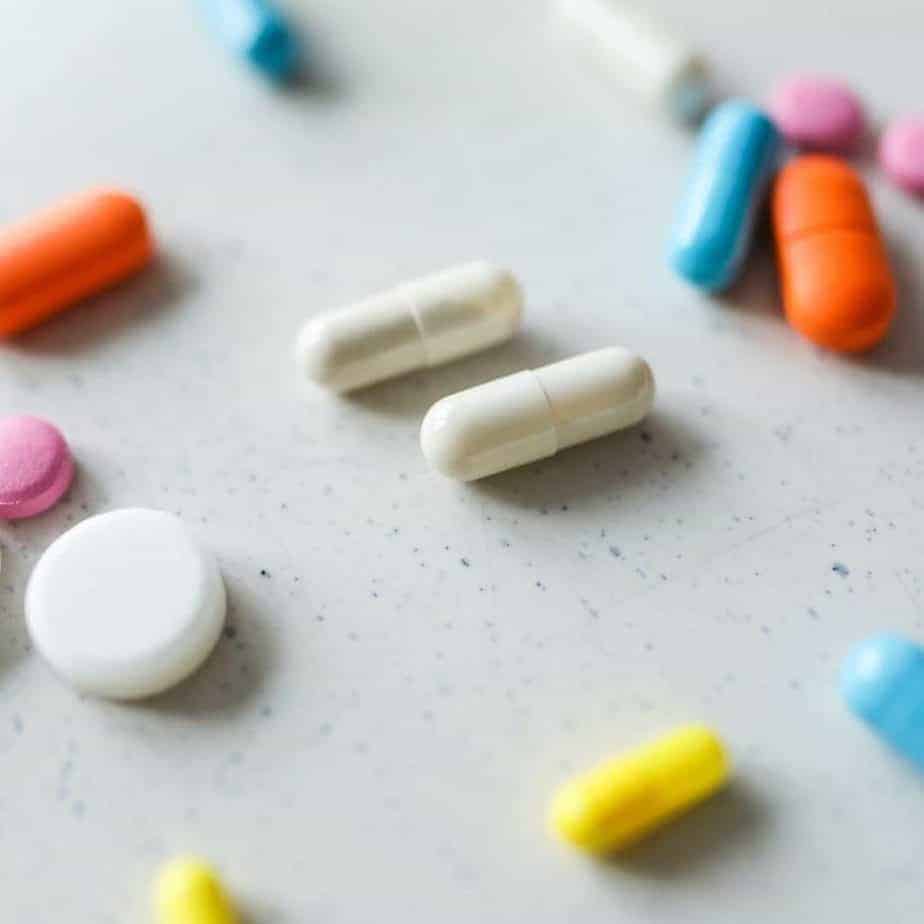

🧡 Individuals Most Vulnerable To A Micronutrient Deficiency Include:
Individuals most at risk of micronutrient deficiency are pregnant women, young children, and the elderly.
Deficiencies can cause birth defects or lead to chronic health problems in children.
The elderly are also at high risk for developing micronutrient deficiencies, because they may have difficulty absorbing food properly or have lost some of their ability to absorb nutrients from food due to age-related diseases.
Moreover, micronutrients in nutrition can happen to anyone who isn't mindful of the proper vitamins and minerals the body needs.
So, this is one of the reasons I created the Eat Your Nutrition website. I want to help others make healthier nutrition choices through education.
Anemia (Iron Or Vitamin B12 Deficiency)
Vitamin B12, also known as cobalamin, is a water-soluble vitamin essential for blood formation, brain function, and nerve function.
Inadequate levels of this vitamin can lead to megaloblastic anemia and other symptoms, such as blood disorders, impaired brain function, and elevated homocysteine levels.
Vitamin B12 deficiency is common, especially in vegetarians, vegans, and older adults. Dietary sources of this vitamin include shellfish, organ meat, meat, eggs, milk products.
Anemia (iron or vitamin B12 deficiency) can be treated with supplements or by replacing lost iron supplies or vitamin B12.
This micronutrient deficiency in nutrition is one of the most common deficiencies in America.
Iodine Deficiency
Stores of iodine vary according to dietary intake and iodine status. Iodine deficiency is a global health problem, particularly during early pregnancy.
A deficiency in iodine is one of the leading causes of preventable brain damage in early childhood.
Many countries of the world have fortified table salt with iodine, because iodine is found naturally in very few foods. Iodine levels are important when thinking about thyroid function.
So if one is deficient in iodine, this can lead to several health concerns surrounding thyroid health.
Recently, lots of individuals have gotten on the health craze of avoiding iodized table salt for pink Himalayan salt. Pink Himalyan salt has other minerals and trace elements, such as potassium, magnesium, and calcium.
However, the extra minerals are in such tiny quantities that the benefits are not as high as people think.
It is important to remember that when choosing pink Himalayan salt, you won't get the extra addition of iodine, so you need to increase your iodine containing foods.
Those foods include seaweed, cod fish and oysters, eggs, and some dairy products, including Greek yogurt and many others.
A huge concern is the addition of anti-caking additives to regular table salt. The FDA has stated that these common additives are safe and pose no risk to individuals. Anti-caking additives are found in many other common pantry items, including baking flours and sugars.
So, the takeaway with salt is that if you replace regular table salt with sea salt, make sure you are aware of adding in foods rich in iodine, like I mentioned above.
The FDA has stated that regular table salt poses no harm to individuals other than the consumption of too much salt into your diet. This can occur regardless of whichever salt you choose, sea salt or table salt.
Vitamin D Deficiency
Vitamin D builds strong bones by helping the body absorb calcium. A deficiency in vitamin D can cause bone diseases, including rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults.
Vitamin D also helps the immune system resist bacteria and viruses
People who are deficient may want to take a supplement or increase their sun exposure and add in more foods containing vitamin D.
It can be found in certain foods, including fatty fish, orange juice, and milks fortified with vitamin D, mushrooms, and egg yolks.
Folate Deficiency
Folate, B9 is a water soluble vitamin naturally found in foods. While folic acid is a synthetic form of the vitamin used in fortified foods and dietary supplements.
Moreover, a folate deficiency during pregnancy has led to associations with low birth weight, preterm delivery, and fetal growth retardation.
Typical symptoms of a folate deficiency include muscle weakness, tiredness, general fatigue, neurological symptoms such as tingling like pins and needles, numbness, and even burning sensations
🥬 Folate Rich Foods
So, to ensure you get enough of your folate intake, try to include some of these foods:
- Dark green leafy vegetables
- Asparagus
- Brussels sprouts
- Peanuts
- Whole grains
- Beans
- Seafood
- Sunflower seeds
Vitamin A Deficiency
This is a fat-soluble vitamin that affects many functions within the body, from the immune function, healthy vision, reproductive issues, and skin health.
Most importantly, a fat-soluble vitamin means you must include some fat into the diet to properly absorb this vitamin.
Vitamin A deficiency is a major cause of childhood morbidity and mortality in the developing world.
However, it is typically not as common in America. This is because the population in most developed countries gets their micronutrients through proper nutrition or supplementation.
Symptoms of a vitamin A deficiency include dry skin, stunted growth in children, acne, infertility, vision problems, such as dry eyes and night blindness.
🥕 Vitamin A Rich Foods
Foods rich in vitamin A include:
- Colorful red, orange and yellow plant foods, such as carrots, sweet potatoes, red and yellow peppers, pumpkin, mango, and tomatoes.
- Beef liver
- Broccoli
- Kale
- Milk
- Eggs
Magnesium Deficiency
This is a key mineral needed for the body. It is an important electrolyte that works with sodium, potassium, and calcium. It helps balance fluids in our cells, tissues, and even our bones.
Magnesium is responsible for roles in blood pressure regulation, heart health, nerve and muscles functions, energy production, bone development, and blood sugar levels.
Low intake and blood levels of magnesium are associated with several conditions, including type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, heart disease, and osteoporosis.
The main symptoms of severe magnesium deficiency include abnormal heart rhythm, muscle cramps, restless leg syndrome, vomiting, loss of appetite, fatigue, migraines. and even tremors and seizures.
So what are some circumstances that can contribute to magnesium deficiency?
Some causes can be diarrhea, malnutrition due to poor living conditions or extreme diets, alcoholism, chemotherapy, use of diuretics, and fat malabsorption issues.
Dietary sources of magnesium include:
- Dark green leafy vegetables like spinach.
- Whole grains
- Beans and legumes like peanuts and lentils.
- Nuts like almonds and cashews.
- Seeds like pumpkin seeds.
- Dark chocolate
🥗 Sufficient Micro Nutrition Through Food
Your best nutrition plan is a good balance between macronutrients, micronutrients and calories. Though micronutrients do not provide a caloric value, they play important roles in various bodily functions.
In addition, because their deficiencies will lead to worsened function, it is important to grant sufficient micro nutrition through your food. Last but not least, micronutrients don't need to be tracked, as long as you consume various foods in decent amounts.
🗣️ Let's Discuss Micronutrients In Nutrition!
So, did you learn any impressive new information about micronutrients and how to avoid them in your diet through nutrition? In most cases, the micronutrients in nutrition can be adequate enough if you eat a balanced healthy diet. In addition, let me know in the comments below.
You can also connect with me @EatYourNutrition on Instagram. I love seeing your photos. #EatYourNutrition #LauraVillanueva
👉 Additional Resources For Holistic Health And Wellness
Also, for further reading and guidance on how to support your holistic lifestyle check out some of my resources below.
Do you struggle to find time to prepare healthy food? Learn how to save time, money, and improve you and your family's health. This 7-day healthy eating plan is exactly the reset for you. Download my guide, 7-Day Healthy Eating Meal Plan.
- Program - Join my Reset & Renew Nutrition Program. Register today.
- Cookbook - Want a cookbook packed with healthy recipes to properly fuel your holistic lifestyle? Order the healthy eating cookbook, Beauty Nutrition Index Cookbook.
- Group Support - Join my Seasonal Nutrition Challenge. All seasonal nutrition challenges come with a meal plan, recipe guide, grocery shopping list, and a seasonal featured nutrition theme.























Comments
No Comments